
Click here for more information on probes and how to order
There are two main modes of thermal resistive probe operation:
- Temperature Contrast Mode: In this mode, the resistive element of Nanonics thermal resistive probe is used as a Pt resistance thermometer. The temperature of the thermal probe changes as the tip scans the surface according to the surface temperature. Change of the Pt wire temperature leads to change of its resistance. The current passed through the probe in temperature contrast mode is set to be small enough that no self-heating of the probe occurs.
- Thermal Conductivity Contrast Mode: In Thermal Conductivity Contrast Mode the resistive element of the Nanonics Thermal Resistive Probe is used as a resistive heater. The constant current passed through the Pt wire is significant and thus the probe temperature is much higher than a sample temperature. When the probe contacts with the sample, heat flows from the probe to the sample which results in the cooling of the probe.
Probe Design
A double-wire cantilevered glass probe has been produced for scanned probe microthermal, resistivity, and topographic measurements. The structure has many potentially unique properties for scanned probe microscopy and other nanotechnological measurements. Double Pt wire probe was fused at the tip and applied to thermal resistive measurements. The probe operation is based on the linear dependence of Pt resistance on temperature.
Key Features
HIGH SENSITIVITY |
Thermal resistive probe has a high sensitivity and microseconds response time due to the nano metric size of the Pt thermal junction. |
EXPOSED THERMAL TIP FOR OPTICAL INTEGRATION |
Provides complete optical access from above and below for full integration with optical microscopes, Raman spectrometers and thus enables combining thermal characterization with optical and spectral mapping. |
MULTIPROBE CAPABILITES |
Cantilevered shape and exposed tip enable to bring the tips of the thermal resistive probe and probe for other SPM methods (AFM, NSOM, Conductive, and Nanoheater) within nanometric distance one to another. The multiprobe capabilities allow to study heat transport properties as function of optical, electrical and other action on the nanoscale level. |
Specificaions:
APPLICATIONS
Temperature Characterization of Photonics Devices
Cleaved face of the 9 m core optical fiber can be imaged in temperature contrast mode using the thermal resistive probes while Nd:YAG laser at 532 nm is transmitted through the fiber. The probe measures the heat distribution at the output of the cleaved fiber. Image below shows thermal distribution in highest optical mode excited in the fiber.
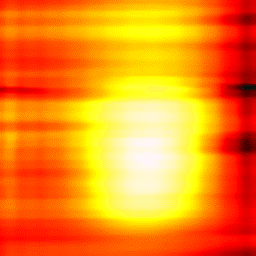
Thermal Conductivity Characterization of the Semiconductor Devices
Thermal conductivity characterization of the polished semiconductor devices
Read more: "Investigating material and functional properties of static random access memories using cantilevered glass multiple-wire force-sensing thermal probes" APL, volume 77, number 26, 25 December 2000 R.Dekhter, E. Khachatryan, Y. Kokotov, and A.Lewis Sophia Kokotov, G. Fish, Y.Shambrot, and K.Lieberman


